The SWIFT BIC code is a standardized international identifier (ISO 9362) used in financial messages exchanges. Understanding what the BIC code is fundamental because it is used to identify entities and to route payments messages over SWIFTNet, the SWIFT secure IP Network. What does BIC stand for? and what is the BIC?
Does BIC stand for “Bank Identifier Code” or”Business Identifier Code”?
At the time this article is written, a search on google with “Bank Identifier Code” (with quotation marks) gives a higher number of results than a search with “Business Identifier Code”. Given these results, one may conclude that BIC stands for Bank Identifier Code. That is what I used to believe until I looked into the standard ISO 9362 which defines the BIC and its structure.
There are different versions of the ISO 9362 standard. In the 1994 version, the BIC code is defined as the Bank Identifier Code. It was the vision of SWIFT and the ISO at that time. When SWIFT introduced the BIC code, it was to be used to identify financial institutions exclusively. But with the time, multinational corporations expressed the need to use the SWIFT Network as well for the communication and exchanges of messages with their banks. These corporations came to be identified by the SWIFT BIC Code as well.
In the revised version of the standard in 2009, the BIC’s definition evolved to meet non financial institutions needs. The acronym BIC stands for Business Identifier Code and has remained the same since then.
SWIFT BIC Codes can be used for the identification of financial and non-financial institutions. Companies and similar entities like Non Governemental Organizations, can therefore be assigned a BIC code. It is SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) which manages the registration of BIC codes and the BIC code repository. This explains why the BIC code is also called SWIFT code, SWIFT ID or SWIFT BIC.
The Business Identifier Code is used to route financial transactions
The SWIFT BIC code is much more than an entity identifier. It is used to route the financial messages from the issuing institution to the receiving institutions. The SWIFT BIC Code therefore plays a crucial role in payment messaging. Wihout it, a message cannot be tranpsorted to the receiving entity over SWIFTNet. SWIFTNet is a global network that interconnects financial institutions all over the world. The BIC code contains the identity and the location of the participants that are used to find out and reach the message destination.
The structure of the SWIFT BIC code
The SWIFT BIC code is composed of exactly 8 or 11 alphanumeric characters structured as followed:
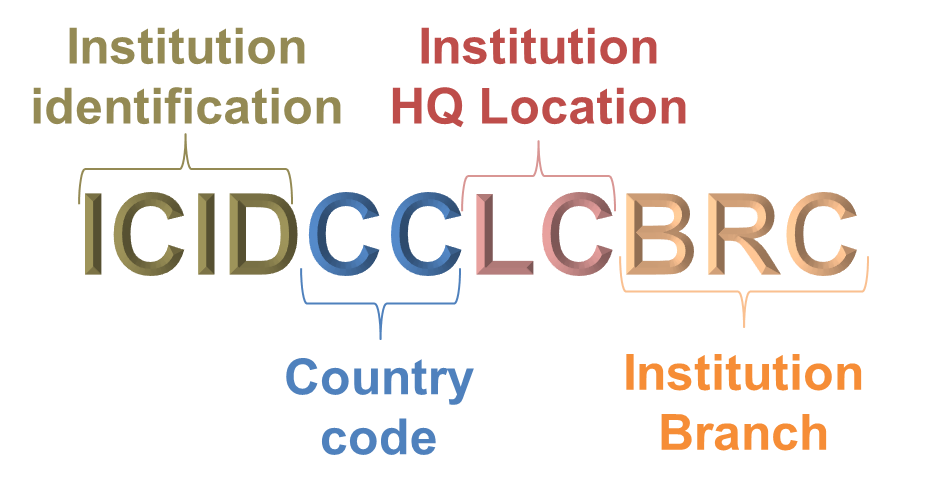
- 4 alphabetical characters that indicate the identification of the institution (bank or coorporate)
- 2 alphabetical characters for the ISO code of the country in which the institution is located
- 2 alphabetic or numeric characters used to locate the institution head office in the country or the head office in a particular region in the country.
- When the second character takes the value “0”, it is typically a test BIC used in test systems as opposed to a BIC used on the live network (also production).
- When the second character takes the value “1”, it denotes a passive participant in the SWIFT network. Passive participants cannot be contacted directly over the SWIFT Network. These BICs are sometimes referred to as ‘BIC1’, ‘non-SWIFT BIC’ and ‘non-connected BIC’. A non-connected BIC is not allowed in the header of a SWIFT message, otherwise the message is rejected by the SWIFT system.
- When second character takes the value “2”, it indicates a reverse billing BIC, where the recipient pays for the message as opposed to the more usual mode where the sender pays for the message.
- 3 alphabetical or numeric characters to indicate a branch or agency of the institution. Unlike the first 8 characters, these last 3 are not mandatory. They are mainly used by banks and less by coorporates. In a
Few examples to illustrate the above explanations:
- DEUTDEFF is the BIC of Deutsche Bank (DEUT) / in Germany (DE) / Main office of Frankfurt (FF)
- DEUTDESS is the BIC of Deutsche Bank (DEUT) / in Germany (DE) / Main office of Stuttgart (SS)
- DEUTDESS648 is the BIC of Deutsche Bank (DEUT) / in Germany (DE) / Main office of Stuttgart (SS). 648 is the branch located in Vaihingen-Enz in the same region.
- DEUTDES0 and DEUTDES0648 are test BIC for DEUTDESS and DEUTDESS648
- LAFAFRPP is the BIC of Lafarge (LAFA) / in France (FF) / Main office of Paris (PP)





